Final Electron Acceptor in Aerobic Respiration
Respiration takes place when any organic compound usually carbohydrate is oxidized completely to CO 2 and H 2 O. Rather an inorganic acceptor such as sulfate SO 4 2- nitrate NO 3 or sulfur S is used.
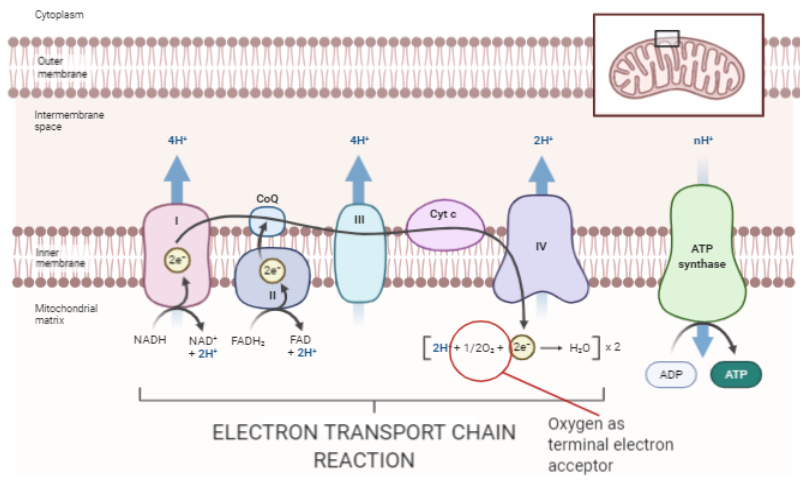
What Compound Is The Terminal Electron Acceptor In Class 11 Biology Cbse
The electrons are passed onto electron carriers which are embedded within the inner mitochondrial membrane and travel along a series of.
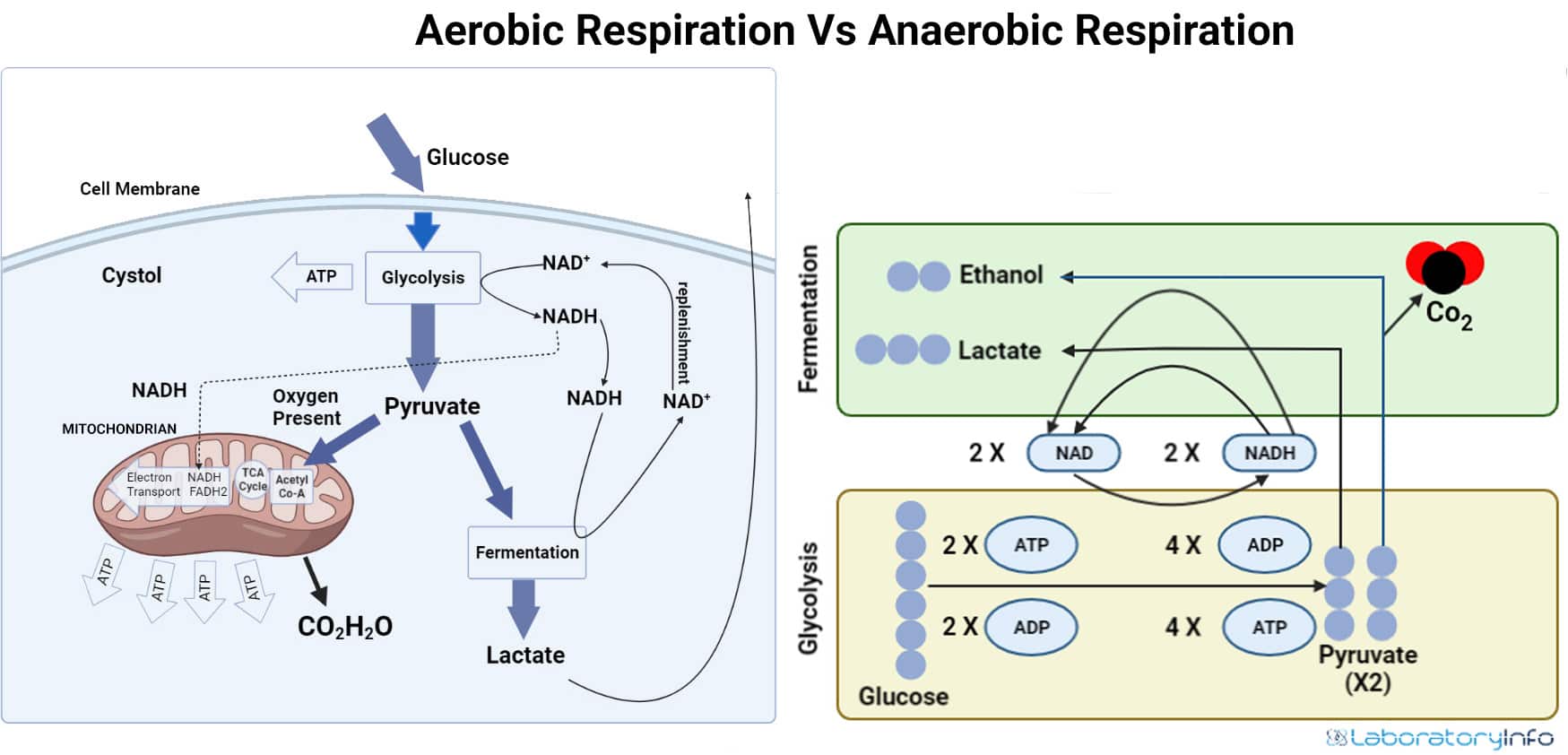
. In this reaction lactic acid replaces oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Aerobic respiration is the most efficient type of cellular respiration which occurs in most eukaryotes and some prokaryotes. And respiratory chain complexes that mirror aerobic respiration in bacteria.
For anaerobic respiration NO 3 SO 4 2 CO 2 or fumarate can serve as terminal electron acceptors rather than O 2 depending on the. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration. Oxidative phosphorylation is the fourth and final step in cellular respiration.
For the electron transport chain to continue working there must be a final electron acceptor. Which is referred to as the final electron acceptor. The oxygen is the final electron acceptor of what is known as the electron transport chain found in the last stage oxidative phosphorylation of aerobic cellular respiration.
Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Oxygen combines with electrons and hydrogen ions to form water one. This transfer of electrons from lower to higher redox potential continues until it reaches the final electron acceptor.
But where does it exactly fit in the picture. The oxygen molecule in aerobic respiration acts as the final electron acceptor resulting in the efficient production of ATP. Oxygen is an essential molecule in cellular respiration.
In the electron transport chain electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to an electron acceptor having a higher redox potential. Because of this oxygen is also called as the final electron acceptor. Basically oxygen can be found at the end of the ETC during aerobic respiration where it accepts electrons while picking up protons in order to produce water molecules.
The electron carriers deposit the electrons at the beginning of the chain and then through a process called chemiosmosis produce many ATP. The ultimate acceptor of these high-energy electrons is oxygen and therefore oxidative phosphorylation generates both ATP and water. Different types of organisms use different types of final electron acceptors.
Mitochondria have two membranes the inner. Oxidative phosphorylation OXPHOS is defined as an electron transfer chain driven by substrate oxidation that is coupled to the synthesis of ATP through an electrochemical transmembrane gradient Figure 131Historically bovine heart mitochondria have been the system of choice for the structural characterization of eukaryotic OXPHOS complexes Saraste 1999 because they. Denitrification is an anaerobic process which converts nitrate to dinitrogen in the following sequence.
It is also called fermentation. The series of reactions is typically shorter in anaerobic respiration and uses a final electron acceptor such as sulfate nitrate sulfur or fumarate instead of oxygen. It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration is used by microorganisms called archaea in which neither oxygen aerobic respiration nor pyruvate derivatives fermentation is the final electron acceptor. Anaerobic respiration also produces less ATP for each sugar molecule digested than aerobic respiration making it a less efficient method of generating cellular energy. For example because erythrocytes red blood cells lack mitochondria they must produce their ATP from anaerobic respiration.
Cellular respiration is of two types ie. The final electron acceptor is not the molecular oxygen as in aerobic respiration. For aerobic organisms oxygen is an absolute requirement for.
Anaerobic respiration occurs in most cells of the body when oxygen is limited or mitochondria are absent or nonfunctional. An important metabolic role of environmental oxygen is to serve as a terminal electron acceptor for the regeneration of NAD via mitochondrial respiration to support cellular oxidation reactions. In aerobic respiration molecular O 2 serves as the terminal acceptor of electrons.
Oxygen provides a force to drive the transport of electrons down the chain. It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Aerobic respiration produces a total of 38 ATP molecules per one molecule.
Madsen in Encyclopedia of Ecology 2008 Denitrification. Oxygen is used by aerobic bacteria during the process of cellular respiration as a final electron acceptor. Methanogenic bacteria are one such type of organisms that use carbon dioxide as the final electron acceptor in the absence of.
If that acceptor is oxygen the process is considered aerobic respiration. NO 3 NO 2 NO N 2 O N 2This dissimilatory process the end product is not assimilated into biomass in which nitrate is used as final electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration is carried. These can be sulfate ions nitrate ions or carbon dioxide.

Aerobic Respiration And Anaerobic Respiration Diagrams Definition And Differences Laboratoryinfo Com
What Is The Terminal Electron Acceptor In Aerobic Cellular Respiration Quora
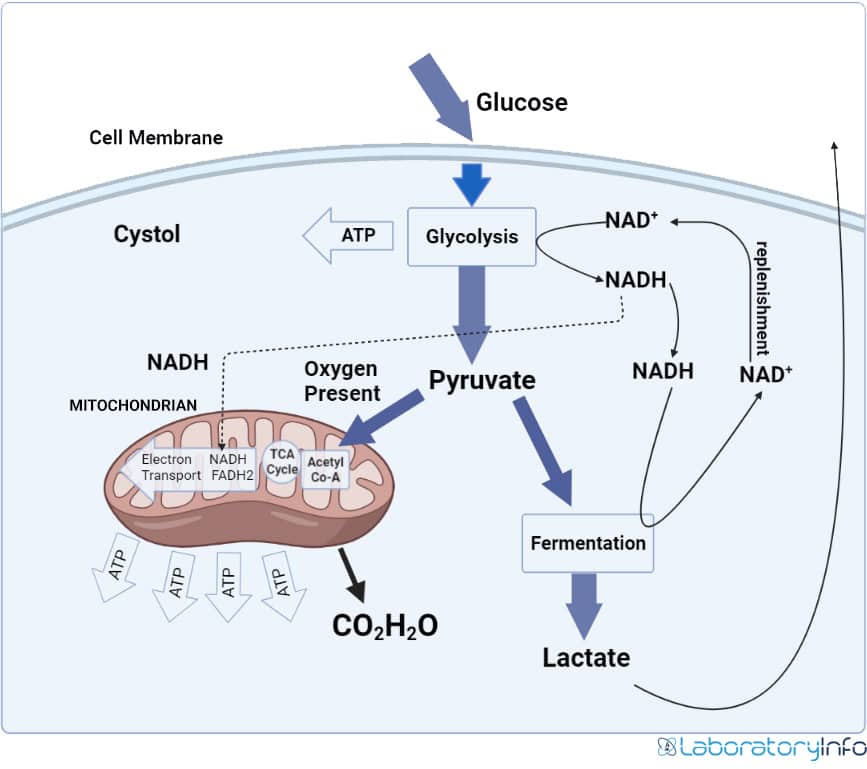
Aerobic Respiration And Anaerobic Respiration Diagrams Definition And Differences Laboratoryinfo Com
0 Response to "Final Electron Acceptor in Aerobic Respiration"
Post a Comment